Henry Ward Beecher said*, “the ability to convert ideas to things is the secret of outward success.” The problem for technologists – people working the technology industry – is not the ability to convert ideas into things; rather, it is having the discipline to select (and focus on) the best ideas.
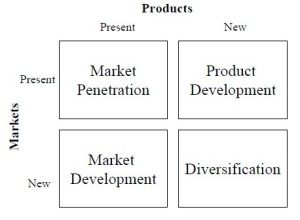
The Ansoff matrix is designed to help business leaders decide where to focus their growth efforts. Specifically, the Ansoff matrix helps you think about what strategy to pursue based on your situation as well as the risks.
Matrix
Application
Market Development
Summary
Selling existing products into new markets.
Goals
- Expand into new/adjacent markets
Key questions
- Do we have the right products? If you have a good mix of products, focus on expanding into related markets. Key indicators would be “ease” of sales process, demand (sold out?).
Tactics
- New geographies
- New segments – ie: target “adjacent” customer-types, demographics, etc
- New distribution channels
Risk
- Riskier than Market Penetration”, but less risky than Diversification
- Greater returns than Market Penetration, but less returns than Diversification
Market Penetration
Summary
Selling existing products into existing markets. These are customers are products that are well-known – the “core business”.
Goals
- Increase or maintain market-share
Key questions
- Does the existing line of business have good (current) growth and strong future growth prospects?
Tactics
- Marketing promotions
- Pricing changes/innovations
- Changes to sales process / additions to sales team
- Acquisitions/consolidation of market
- Increase usage of existing customers
- Loyalty programs
Risk
- Least risky, lower growth returns (generally)
Product Development
Summary
Selling new products to existing markets. This could include new products as well as incremental changes (modified) to existing products. Well-suited for a business where competition is strong and there is a strong-need for competitive differentiation.
Goals
- Develop new products to serve existing customers
- Incremental changes targeted at existing customers
Key questions
- Are current customers requesting (demanding?) features/products that we don’t currently offer?
Tactics
- Develop new/related products
- Extend product to include new features
- Market research, R&D, customer needs analysis
Risk
- Riskier than Market Penetration”, but less risky than Diversification
- Greater returns than Market Penetration, but less returns than Diversification
Diversification
Summary
Selling new products to new markets. This can be the most-rewarding approach; however, it is the riskiest approach because you do not have experience with this market/product-type.
Goals
- Break-through/transformational growth
- Main advantage is to “spread risk” away from core business – if “core” business fails, the new business can replace losses to the core
Key questions
- Are your current markets growing?
- Are your products well-positioned for future growth?
- Is there a high-level of risk associated with your core business?
Tactics
- Market research / R&D
- New product development methodologies
Risk
- Highest risk, highest reward potential
Sources: